The Ultimate Guide to Retractor Instruments in the Medical Field
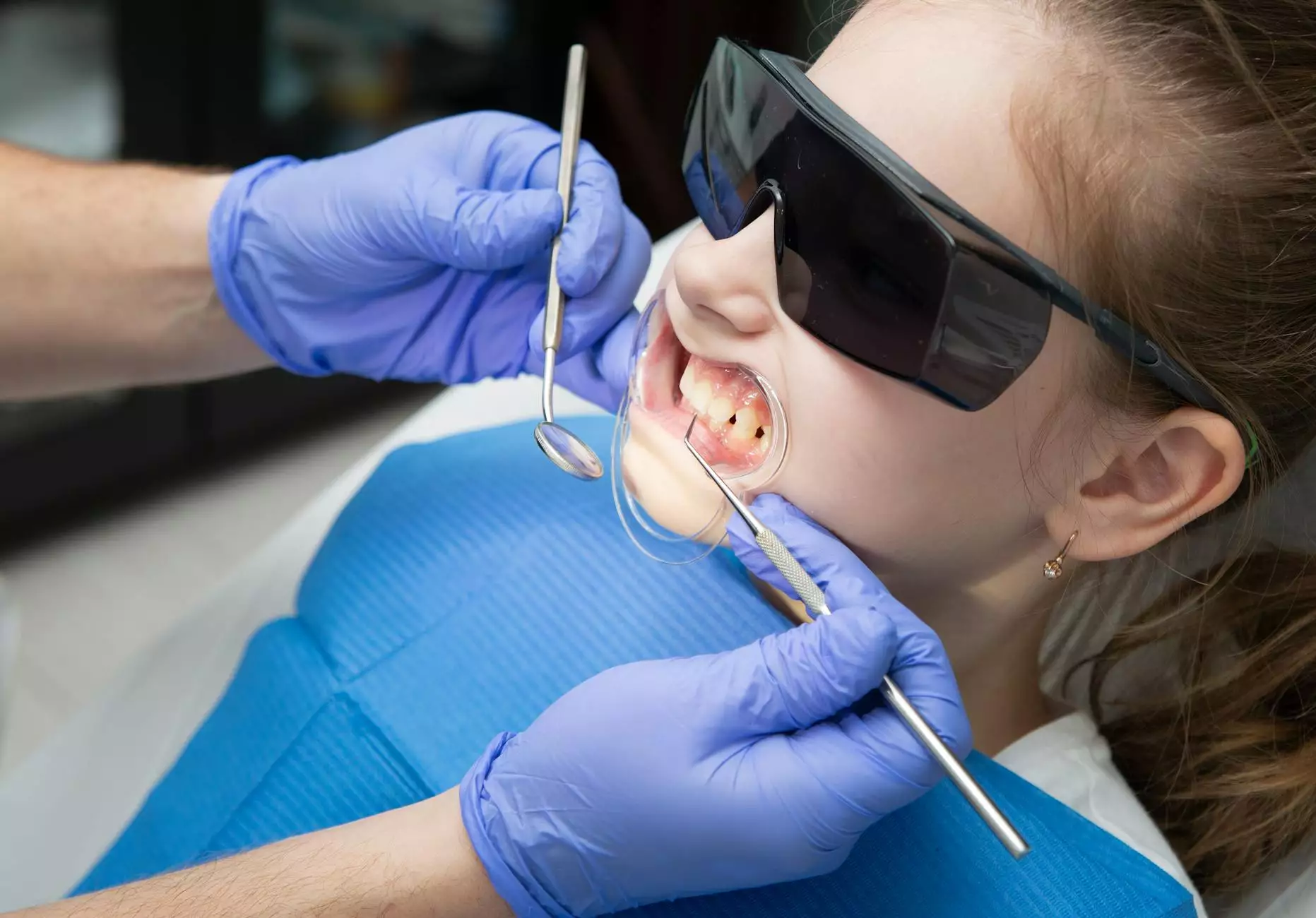
In the ever-evolving world of health and medical supplies, the significance of surgical instruments cannot be understated. Among these instruments, the retractor instrument plays a crucial role in modern surgery and medical procedures. This guide explores everything you need to know about retractor instruments, their types, uses, and the impact they have in various health markets.
Understanding the Retractor Instrument
A retractor instrument is designed to hold back tissues and organs, providing surgeons with unobstructed access to the surgical site. This action is not only central to the efficiency of surgical interventions but is also fundamental to enhancing patient safety during operations. By keeping the area clear, retractors facilitate better visibility and precision, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Importance of Retractor Instruments in Surgery
Retractors are indispensable tools in the surgical toolkit for several reasons, including:
- Enhanced Visibility: By holding back tissues, retractors expose the surgical field, allowing surgeons to work with greater accuracy.
- Improved Accessibility: Certain surgical sites can be hard to access, and retractors help in maintaining the necessary space for surgical procedures.
- Reduced Tissue Trauma: Many modern retractors are designed to minimize injury to surrounding tissues, reducing recovery time and postoperative complications.
- Versatile Use: Retractors are utilized across various surgical specialties, including orthopedic, cardiovascular, and neurological surgery.
Types of Retractor Instruments
Retractor instruments can be classified based on their design and intended application. Here are the most common types:
1. Handheld Retractors
Handheld retractors require a surgical assistant to hold them in place during the procedure. Some popular examples include:
- Deavers Retractor: Ideal for retracting deep abdominal incisions.
- Army-Navy Retractor: Commonly used for shallow incisions across multiple surgical fields.
- Simon Retractor: Helps in orthopedic surgeries by providing increased exposure in the surgical area.
2. Self-Retaining Retractors
These instruments have adjustable arms that keep them in position without the need for assistance. Notable examples are:
- Cheatle Retractor: Frequently used in operations requiring full access to the abdomen or thoracic cavity.
- Balfour Retractor: Equipped with locking mechanisms, ideal for retaining wide exposures in pelvic surgery.
- Finochietto Retractor: Common in thoracic surgery for expanding the chest wall.
3. Specialty Retractors
These may be designed for specific applications or body parts. Examples include:
- Ophthalmic Retractors: Used in eye surgeries.
- Vascular Retractors: Designed to expose blood vessels during cardiovascular surgeries.
Material and Design Considerations
The effectiveness of a retractor instrument lies not only in its design but also in the materials used for its construction. Stainless steel is a commonly used material, renowned for its durability and resistance to corrosion. Advanced retractors may also incorporate non-allergenic materials or coatings to ensure patient safety and comfort.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Retractor Instruments
With technological advancements, retractors have evolved significantly. Some of the innovations include:
- Lighted Retractors: These instruments come with built-in lighting, which enhances visibility in complicated procedures.
- Robot-Assisted Retractors: Integration of robotics in surgery has led to the development of retractors that can be controlled with precision by surgeons through robotic systems.
- Adjustable Mechanisms: Modern self-retaining retractors now have more ergonomic and adjustable features, allowing for quick repositioning during surgery.
Choosing the Right Retractor Instrument
When it comes to selecting the appropriate retractor instrument, several factors should be considered:
- Surgical Specialty: Different branches of surgery require different types of retractors.
- Incision Size: The size and depth of the incision dictate the type of retractor needed.
- Surgeon Preference: Individual surgeons may have preferences for specific instruments based on their past experiences and ease of use.
- Patient Considerations: Variations in patient anatomy may influence the choice of retractor.
Conclusion
The importance of retractor instruments in the surgical field cannot be overlooked. From enhancing visibility to improving patient safety, their role is integral to successful surgical outcomes. As advancements in technology continue to evolve, the capabilities and effectiveness of these instruments will undoubtedly improve, further transforming the health and medical landscape.
For healthcare professionals seeking high-quality surgical supplies, new-medinstruments.com offers a wide range of both handheld and self-retaining retractors, ensuring that every surgical need is met with precision and quality. Investing in the right instruments can help elevate surgical practices and enhance patient care.









